Getting Started
VtlProcessing is a .NET Core library, which allows to perform translations between VTL and selected target languages. In this step-by-step guide we will create a simple console application utilizing VTL Processing to generate T-SQL target code from VTL source. VtlProcessing provides support for .NET Core IoC containers. However, in this guide we will use different, simplified set of API. This is the provided facade class.
Project setup
VtlProcessing is divided into few modules:
-
VtlProcessing.Core - transformation od VTL expressions to the form of intermediate representation (IR)
-
VtlProcessing.Targets.TSQL - generation of Transact SQL target code from supplied IR objects
-
VtlProcessing.Targets.PlantUml - generation of Transact SQL target code from supplied IR objects, helps to visualize and debug VTL code
Each of these modules has separate Nuget package and need to be referenced individually.
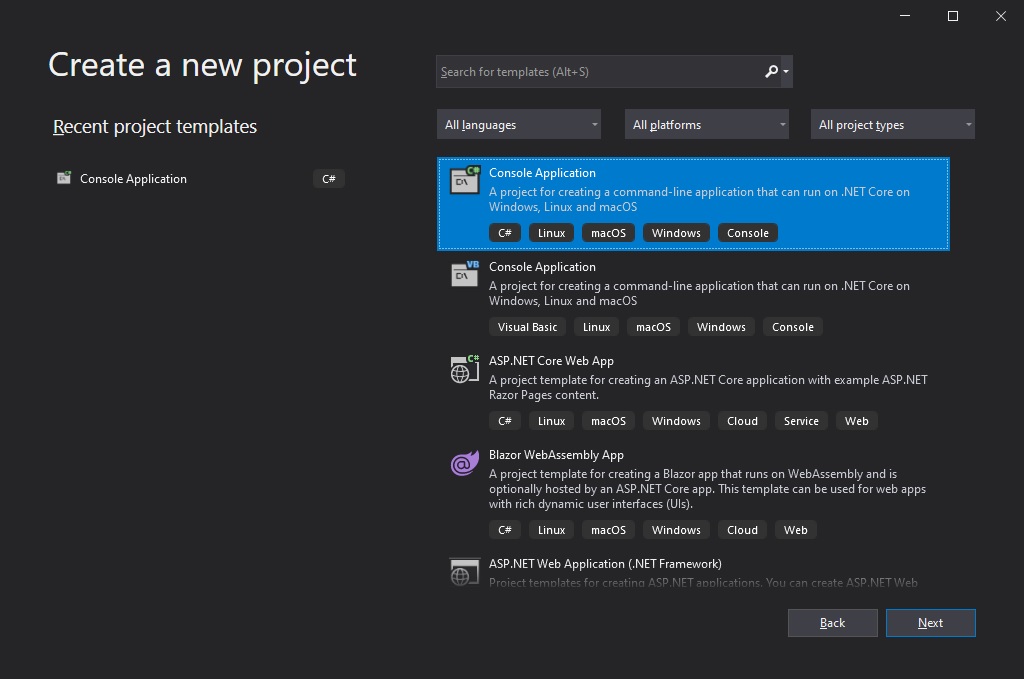
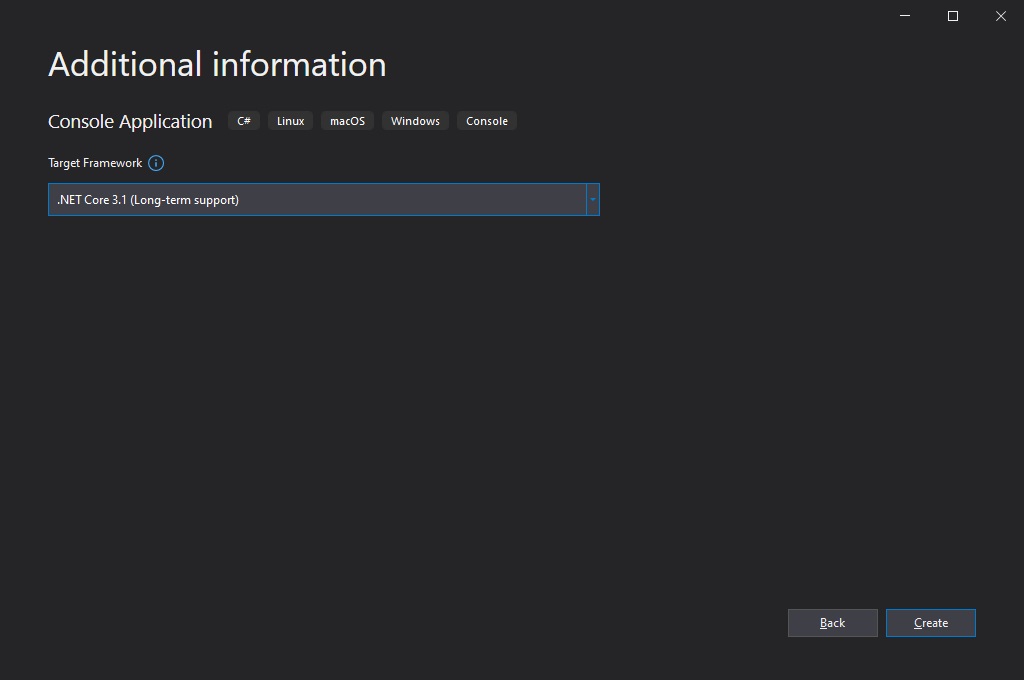
Let’s start by creating new console application .Net Core 3.1 project.
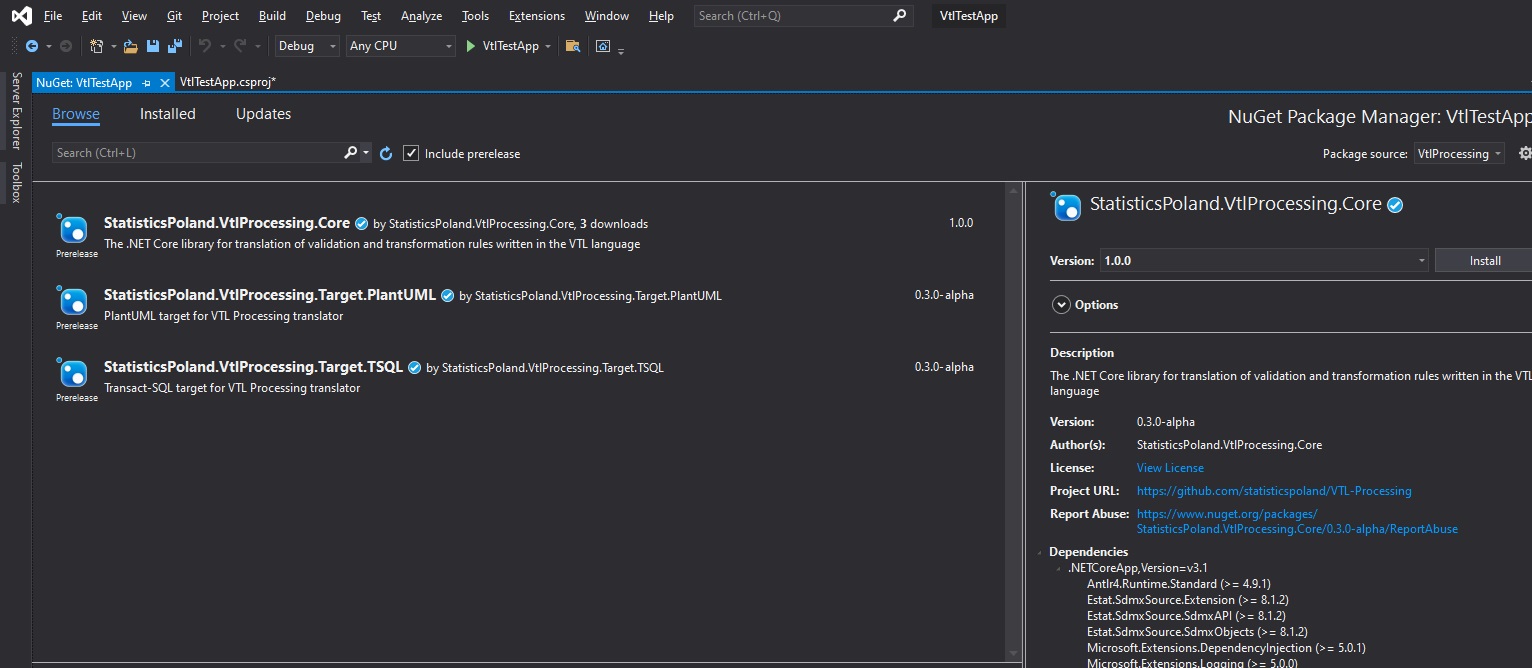
Next, add required VtlProcessing dependencies. We will need two Nuget packages: StatisticsPoland.VtlProcessing.Core and StatisticsPoland.VtlProcessing.Targets.TSQL
Create and configure translator
With dependencies added, let’s create a new object of class Translator. It is found in the "StatisticsPoland.VtlProcessing.Core" namespace.
using StatisticsPoland.VtlProcessing.Core;
namespace VtlTestApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Translator translator = new Translator((configure) =>
{
});
}
}
}Next, we need to configure the use of the T-SQL translation target language. If we want comments to be generated in target code, include appropriate setting.
...
using StatisticsPoland.VtlProcessing.Target.TSQL.Infrastructure;
namespace VtlTestApp
{ ...Translator translator = new Translator((configure) =>
{
configure.AddTsqlTarget((config) =>
{
config.AddComments();
});
});Setup data model
The translation process need information about data structures it will work with. This need to be configured. In our simple case, we will use a json file containing all necessary metadata. Let’s create an empty DataModel.json file.
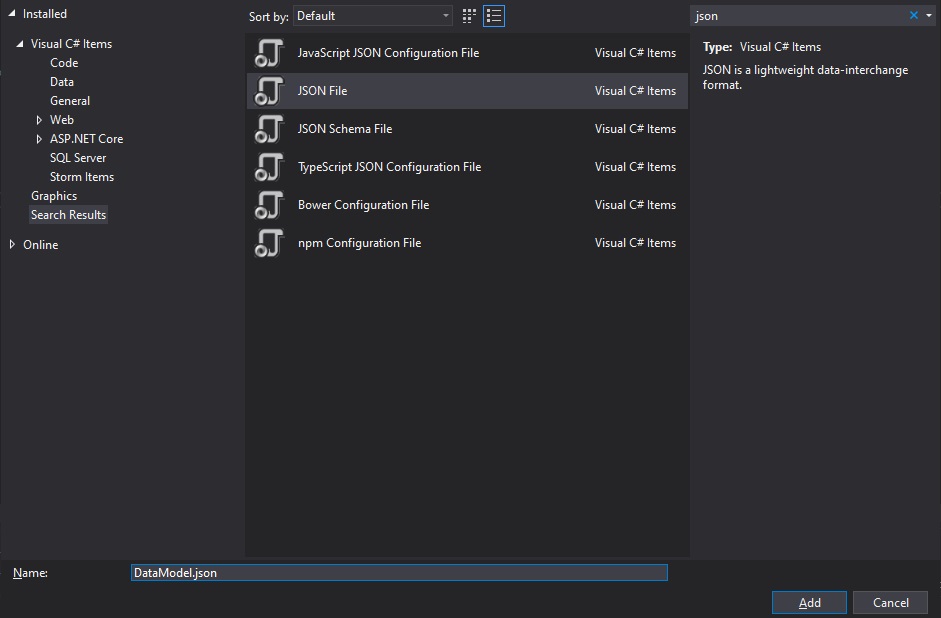
Paste the following content into the DataModel.json file.
{
"DataModel": {
"Namespace": "JsonTest",
"DataStructuresCollection": [
{
"DatasetName": "X",
"Identifiers": [
{
"BaseComponentName": "Id1",
"ComponentName": "Id1",
"ValueDomain": {
"Signature": "integer_default"
}
}
],
"Measures": [
{
"BaseComponentName": "Me1",
"ComponentName": "Me1",
"ValueDomain": {
"Signature": "integer_default"
}
},
{
"BaseComponentName": "Me2",
"ComponentName": "Me2",
"ValueDomain": {
"Signature": "integer_default"
}
}
],
"ViralAttributes":
[
{
"BaseComponentName": "At1",
"ComponentName": "At1",
"ValueDomain": {
"Signature": "string_default"
}
}
]
}
{
"DatasetName": "Y",
"Identifiers": [
{
"BaseComponentName": "Id1",
"ComponentName": "Id1",
"ValueDomain": {
"Signature": "integer_default"
}
},
{
"BaseComponentName": "Id2",
"ComponentName": "Id2",
"ValueDomain": {
"Signature": "integer_default"
}
}
],
"Measures": [
{
"BaseComponentName": "Me1",
"ComponentName": "Me1",
"ValueDomain": {
"Signature": "integer_default"
}
},
{
"BaseComponentName": "Me2",
"ComponentName": "Me2",
"ValueDomain": {
"Signature": "number_default"
}
}
]
}
]
}
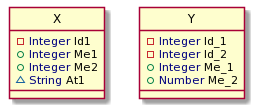
}It holds all necessary structure metadata about two datasets X and Y in data model namespace JsonTest. It can be visualized as following:
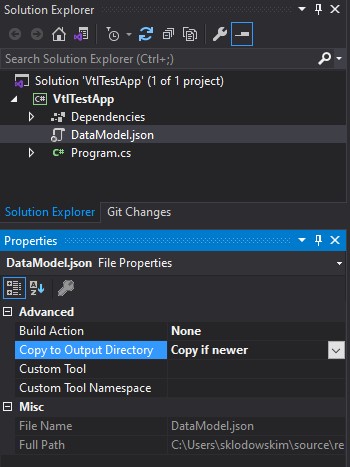
Set Copy to Output Directory property to Copy if newer value.
Next, we need to link our Json file as a data model source to the translator object. Also set the default namespace used by the translator to "JsonTest".
...
using StatisticsPoland.VtlProcessing.Core.DataModelProviders;
using System.IO;
namespace VtlTestApp
{ ...translator.DataModels.AddJsonModel($"{Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()}\\DataModel.json");
translator.DataModels.DefaultNamespace = "JsonTest";Setup environment mapping
Next phase is to configure environment mapper of the translator.
It can be done by providing a Dictionary<string, string> object.
In the following example we will map JsonTests namespace to the SqlDatabase schema of the target database.
...
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace VtlTestApp
{ ...translator.EnvironmentMapper.Mapping = new Dictionary<string, string>()
{
{ "JsonTest", "[SqlDatabase]." }
};Run translation
Translator object is now ready to use.
Let’s do the translation of simple VTL expression: Z := X + Y
Just call the Translate method to get the result string containing executable T-SQL code.
Finally, we put the result into the console output.
...
using System;
namespace VtlTestApp
{ ...string vtlSource = "Z := X + Y";
string tsqlResult = translator.Translate(vtlSource, "TSQL");
Console.WriteLine(tsqlResult);The printed result should look like the following:
-- Script generated: 23.07.2021 12:13:04
BEGIN TRANSACTION
IF OBJECT_ID (N'tempdb..#Z', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE #Z
-- Raw: Z := X + Y
SELECT * INTO #Z FROM (
SELECT
ds1.Id1,
ds2.Id2,
ds1.Me1 + ds2.Me1 AS Me1,
ds1.Me2 + ds2.Me2 AS Me2,
(SELECT MIN(VALUE) FROM
(SELECT ds1.At1 AS VALUE UNION
SELECT ds2.At1 AS VALUE) AS t) AS At1
FROM [SqlDatabase].X AS ds1
INNER JOIN [SqlDatabase].Y AS ds2
ON
ds1.Id1 = ds2.Id1
) AS t
COMMIT TRANSACTION
GOComplete sample
Here we have complete source code of sample application:
using StatisticsPoland.VtlProcessing.Core.DataModelProviders;
using StatisticsPoland.VtlProcessing.Core.UserInterface;
using StatisticsPoland.VtlProcessing.Target.TSQL.Infrastructure;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
namespace VtlTestApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Translator translator = new Translator((configure) =>
{
configure.AddTsqlTarget((config) =>
{
config.AddComments();
});
});
translator.DataModels.AddJsonModel(
$"{Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()}\\DataModel.json");
translator.DataModels.DefaultNamespace = "JsonTest";
translator.EnvironmentMapper.Mapping = new Dictionary<string, string>()
{
{ "JsonTest", "[SqlDatabase]." }
};
string vtlSource = "Z := X + Y";
string tsqlResult = translator.Translate(vtlSource, "TSQL");
Console.WriteLine(tsqlResult);
}
}
}